Efficiency wages minimum-wage laws and unions all keep wages – Efficiency wages, minimum wage laws, and unions are three factors that can significantly influence wages. This article explores the concept of efficiency wages and how they impact labor productivity, analyzes the effects of minimum-wage laws on labor market outcomes, and examines the role of unions in wage determination.
We will also explore the interactions and trade-offs between these factors and discuss the implications for labor market policies.
Efficiency Wages
Efficiency wages are wages that are paid above the market equilibrium wage. They are designed to increase worker productivity and reduce turnover. There are several theories about why efficiency wages work. One theory is that workers who are paid more are more likely to be motivated and productive.
Another theory is that workers who are paid more are less likely to quit their jobs, which reduces turnover costs for the employer.
Efficiency wages are prevalent in a variety of industries and occupations. Some examples include:
- High-skilled occupations, such as engineers and doctors
- Occupations that require a lot of training, such as pilots and nurses
- Industries with high turnover rates, such as retail and hospitality
Efficiency wages have a number of potential benefits. They can increase worker productivity, reduce turnover, and improve morale. However, they can also be expensive for employers. It is important to weigh the costs and benefits of efficiency wages before implementing them.
Minimum-Wage Laws
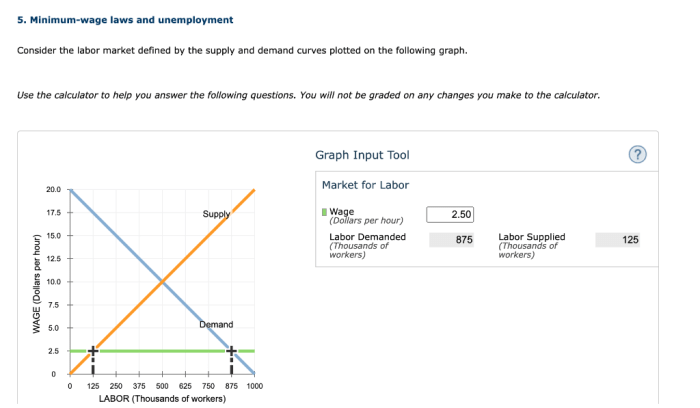
Minimum-wage laws set a minimum wage that employers must pay their workers. The effects of minimum-wage laws on labor market outcomes are complex and have been the subject of much debate. Some studies have found that minimum-wage laws can lead to job losses, while others have found that they have little or no impact on employment.
The effects of minimum-wage laws on wages are more clear-cut. Studies have consistently found that minimum-wage laws lead to higher wages for low-wage workers.
There are a number of arguments for and against raising the minimum wage. Proponents of raising the minimum wage argue that it will help to reduce poverty and inequality. They also argue that it will boost consumer spending and stimulate the economy.
Opponents of raising the minimum wage argue that it will lead to job losses and higher prices. They also argue that it will make it more difficult for small businesses to compete.
The evidence on the impact of minimum-wage laws is mixed. Some studies have found that minimum-wage laws can lead to job losses, while others have found that they have little or no impact on employment. The effects of minimum-wage laws on wages are more clear-cut.
Studies have consistently found that minimum-wage laws lead to higher wages for low-wage workers.
Unions

Unions are organizations that represent workers in collective bargaining with employers. Unions negotiate wages, working conditions, and other benefits for their members. Unions can have a significant impact on wages and working conditions. Studies have shown that unionized workers earn higher wages and have better working conditions than non-unionized workers.
Unions play a vital role in collective bargaining. They represent workers in negotiations with employers over wages, working conditions, and other benefits. Unions also provide a voice for workers on the job. They can help to ensure that workers are treated fairly and that their rights are protected.
Unions have a strong presence in a number of industries, including manufacturing, construction, and transportation. In some industries, such as the public sector, unions represent a majority of workers.
Interactions and Trade-offs: Efficiency Wages Minimum-wage Laws And Unions All Keep Wages
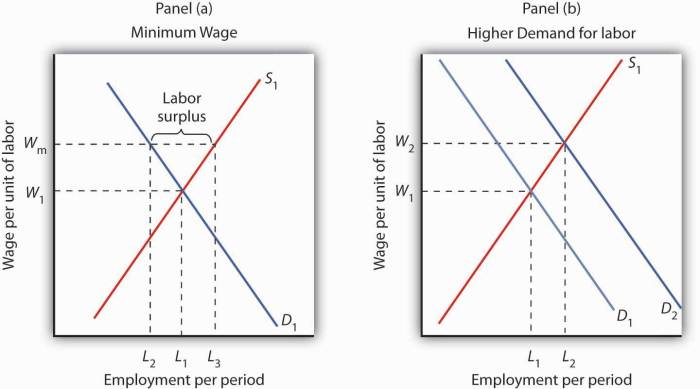
The interactions between efficiency wages, minimum-wage laws, and unions are complex. Efficiency wages and minimum-wage laws can both lead to higher wages for workers. However, efficiency wages can also lead to job losses, while minimum-wage laws can have little or no impact on employment.
Unions can help to offset the negative effects of efficiency wages and minimum-wage laws by negotiating higher wages and better working conditions for their members.
There are a number of trade-offs involved in designing labor market policies that consider efficiency wages, minimum-wage laws, and unions. One trade-off is between the goal of increasing wages for low-wage workers and the goal of minimizing job losses. Another trade-off is between the goal of increasing worker productivity and the goal of reducing inequality.
It is important to weigh the costs and benefits of different labor market policies before implementing them. There is no one-size-fits-all solution, and the best policy will vary depending on the specific circumstances.
User Queries
What are efficiency wages?
Efficiency wages are wages that are higher than the market-clearing wage. They are paid by employers to increase worker productivity.
What are the effects of minimum wage laws?
Minimum wage laws can have a variety of effects on labor market outcomes, including increasing wages for low-wage workers, reducing employment, and increasing inequality.
How do unions influence wages?
Unions can influence wages through collective bargaining. They can negotiate with employers for higher wages, better benefits, and improved working conditions.