Kinetic energy and potential energy venn diagram provide a powerful tool for understanding the relationship between these two fundamental forms of energy. In this article, we will delve into the concepts of kinetic and potential energy, explore their intersections through a Venn diagram, and examine their applications in everyday life.
This comprehensive guide will provide a clear and structured understanding of the topic, making it accessible to readers of all levels.
Kinetic Energy and Potential Energy: Definitions and Formulas
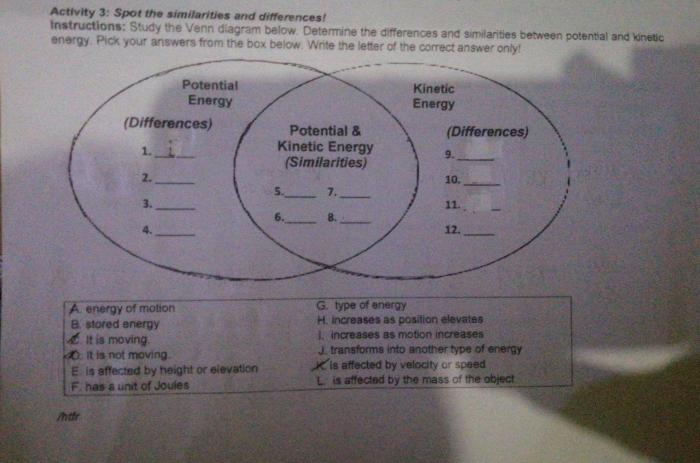
Kinetic energy and potential energy are two fundamental forms of energy that describe the state of an object. Kinetic energy is the energy an object possesses due to its motion, while potential energy is the energy an object possesses due to its position or state.
Kinetic Energy
Kinetic energy (KE) is calculated using the formula:
KE = 1/2 mv^2
Where:
- KE is kinetic energy in joules (J)
- m is the mass of the object in kilograms (kg)
- v is the velocity of the object in meters per second (m/s)
Potential Energy
Potential energy (PE) is calculated using the formula:
PE = mgh
Where:
- PE is potential energy in joules (J)
- m is the mass of the object in kilograms (kg)
- g is the acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s^2)
- h is the height of the object above a reference point in meters (m)
Venn Diagram: Structure and Intersections
A Venn diagram is a graphical representation that shows the relationships between different sets. In the context of kinetic and potential energy, a Venn diagram can be used to illustrate how these two forms of energy can coexist within an object.
Structure of a Venn Diagram
A Venn diagram consists of two or more overlapping circles. Each circle represents a different set, and the overlapping area represents the intersection of the two sets.
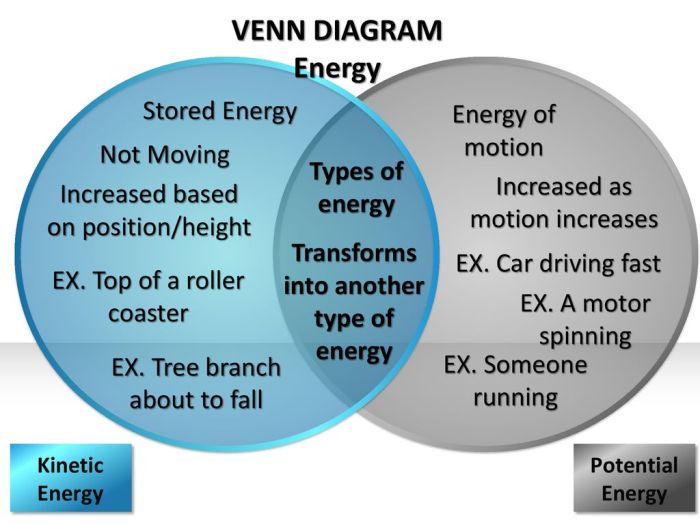
Intersection of Kinetic and Potential Energy
In a Venn diagram, the intersection of kinetic and potential energy represents the energy an object possesses due to both its motion and its position or state. For example, a ball thrown into the air possesses both kinetic energy due to its motion and potential energy due to its height above the ground.
Examples of Kinetic and Potential Energy: Kinetic Energy And Potential Energy Venn Diagram
Objects Possessing Kinetic Energy, Kinetic energy and potential energy venn diagram
- A moving car
- A rolling ball
- A flowing river
- A vibrating guitar string
Objects Possessing Potential Energy
- A ball held above the ground
- A stretched rubber band
- Water stored in a reservoir
- A compressed spring
Conversion between Kinetic and Potential Energy
Kinetic energy and potential energy can be converted into each other. When an object moves, its kinetic energy increases while its potential energy decreases. Conversely, when an object comes to rest, its kinetic energy decreases while its potential energy increases.
Conversion of Kinetic Energy to Potential Energy
- A ball thrown into the air gains potential energy as it rises and loses kinetic energy as it slows down.
- A car climbing a hill gains potential energy as it loses kinetic energy.
Conversion of Potential Energy to Kinetic Energy
- A ball falling from a height gains kinetic energy as it loses potential energy.
- A car rolling down a hill gains kinetic energy as it loses potential energy.
Applications of Kinetic and Potential Energy
Kinetic and potential energy play a significant role in many aspects of everyday life.
Applications of Kinetic Energy
- The kinetic energy of moving vehicles is used to transport goods and people.
- The kinetic energy of wind turbines is used to generate electricity.
- The kinetic energy of water flowing through a dam is used to generate hydroelectric power.
Applications of Potential Energy
- The potential energy of water stored in reservoirs is used to generate hydroelectric power.
- The potential energy of stretched rubber bands is used in elastic bands and slingshots.
- The potential energy of compressed springs is used in springs, shock absorbers, and toys.
Expert Answers
What is the difference between kinetic energy and potential energy?
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion, while potential energy is the energy stored within an object due to its position or condition.
How can kinetic energy be converted into potential energy?
Kinetic energy can be converted into potential energy by doing work against a force, such as lifting an object against gravity.
What are some examples of objects possessing potential energy?
Examples of objects possessing potential energy include a stretched rubber band, a raised object, or a charged capacitor.