Worksheet Structure of DNA and Replication: A Comprehensive Guide explores the fundamental principles of DNA structure and replication, providing a comprehensive understanding of these critical biological processes.
DNA, the blueprint of life, is a complex molecule that carries genetic information essential for the development, function, and reproduction of all living organisms. Understanding its structure and the process of replication is crucial for unraveling the mysteries of life and unlocking new possibilities in biotechnology and medicine.
Introduction
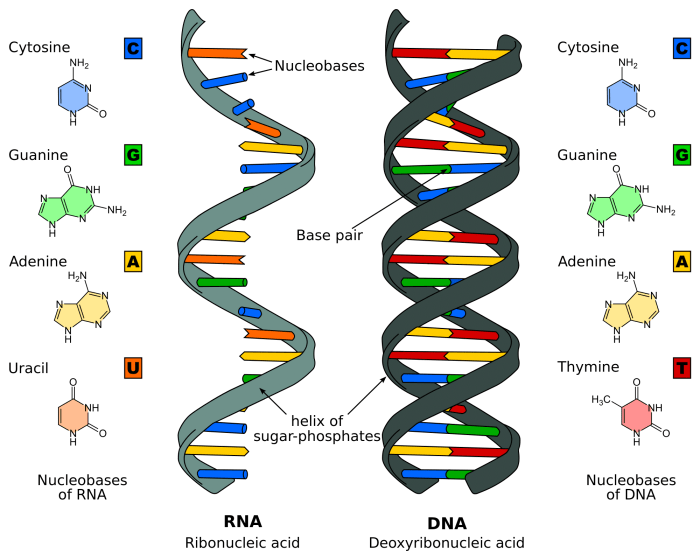
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is a molecule that contains the instructions for an organism’s development and characteristics. It is made up of four different types of nucleotides: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). These nucleotides are arranged in a specific order to form genes, which are the units of heredity.
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes a copy of its DNA. This process is essential for cell division and for the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next.
Components of DNA
The basic components of DNA are nucleotides. Nucleotides are made up of a nitrogenous base, a deoxyribose sugar, and a phosphate group. The nitrogenous bases are adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine. The deoxyribose sugar is a five-carbon sugar. The phosphate group is a negatively charged molecule.The
nucleotides are arranged in a specific order to form genes. Genes are the units of heredity. They contain the instructions for making proteins. Proteins are the building blocks of cells and tissues.
DNA Structure, Worksheet structure of dna and replication
DNA is a double helix. This means that it is made up of two strands of nucleotides that are twisted around each other. The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases. The nitrogenous bases are complementary to each other.
This means that adenine always pairs with thymine, and cytosine always pairs with guanine.
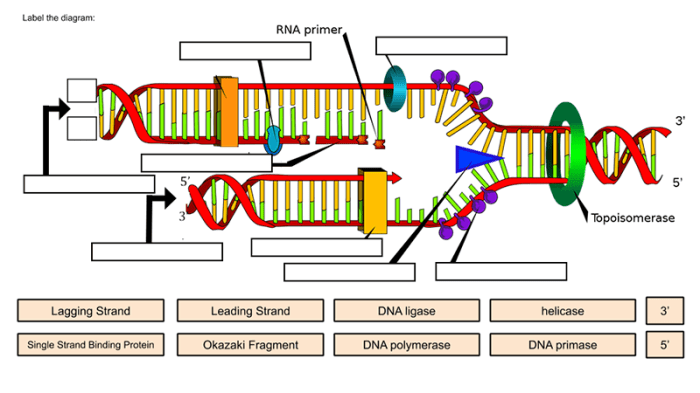
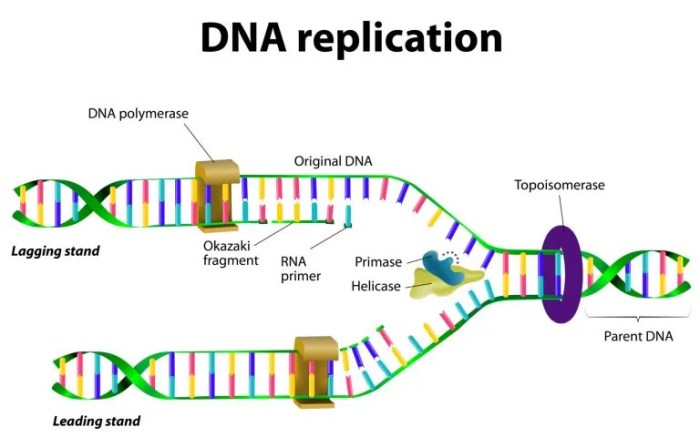
Replication Process
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes a copy of its DNA. This process is essential for cell division and for the transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next.DNA replication begins when the DNA double helix unwinds.
This process is carried out by an enzyme called helicase. Once the DNA double helix is unwound, the two strands are separated. Each strand of DNA then serves as a template for the synthesis of a new strand of DNA.
This process is carried out by an enzyme called DNA polymerase.DNA polymerase adds nucleotides to the new strand of DNA in a specific order. The order of the nucleotides is determined by the order of the nucleotides in the template strand.
Once the new strand of DNA is complete, it is annealed to the template strand. This process is carried out by an enzyme called ligase.
Errors in Replication
DNA replication is a very accurate process, but errors can occur. These errors can be caused by a variety of factors, including radiation, chemicals, and viruses. Errors in DNA replication can lead to mutations. Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence.
Mutations can be harmful, beneficial, or neutral.
Applications of DNA Structure and Replication: Worksheet Structure Of Dna And Replication
Knowledge of DNA structure and replication has a wide range of applications in biotechnology and medicine. For example, DNA replication is used to amplify DNA samples for use in DNA fingerprinting and genetic testing. DNA replication is also used to produce genetically modified organisms (GMOs).
GMOs are organisms whose DNA has been altered in a laboratory. GMOs are used to produce a variety of products, including pharmaceuticals, food, and biofuels.
Question Bank
What are the basic components of DNA?
DNA consists of nucleotides, which are composed of a sugar molecule (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine).
How does DNA replication occur?
DNA replication involves three main steps: initiation, elongation, and termination. During initiation, the DNA double helix unwinds, and the enzyme helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between base pairs. DNA polymerase then adds complementary nucleotides to each exposed strand, elongating the new DNA molecules.
Finally, ligase joins the newly synthesized DNA fragments together.
What is the importance of DNA structure and replication?
Understanding DNA structure and replication is crucial for comprehending genetic inheritance, disease mechanisms, and developing new therapeutic strategies. It also plays a vital role in biotechnology applications, such as genetic engineering and DNA fingerprinting.