Chapter 11 the cardiovascular system answer key – Chapter 11: The Cardiovascular System Answer Key unlocks the mysteries of this vital system, providing a comprehensive guide to its structure, function, and disorders.
Delve into the intricacies of the heart, blood vessels, and blood, as well as the intricate regulation of heart rate and blood pressure. Discover the mechanisms behind common cardiovascular disorders and explore the diagnostic and treatment options available.
1. Cardiovascular System Structure and Function: Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Answer Key
The cardiovascular system is a complex network of organs and vessels that transport blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues and removing waste products. Its components include the heart, blood vessels (arteries, veins, and capillaries), and blood.
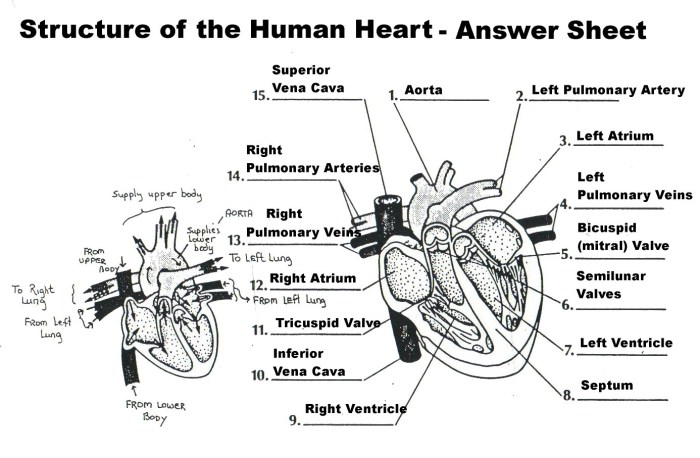
1.1 The Heart
The heart is a muscular organ located in the chest cavity. It pumps blood through the body by contracting and relaxing in a rhythmic cycle. The heart has four chambers: two atria (upper chambers) and two ventricles (lower chambers). Blood flows into the atria, then into the ventricles, and is pumped out to the body through the arteries.
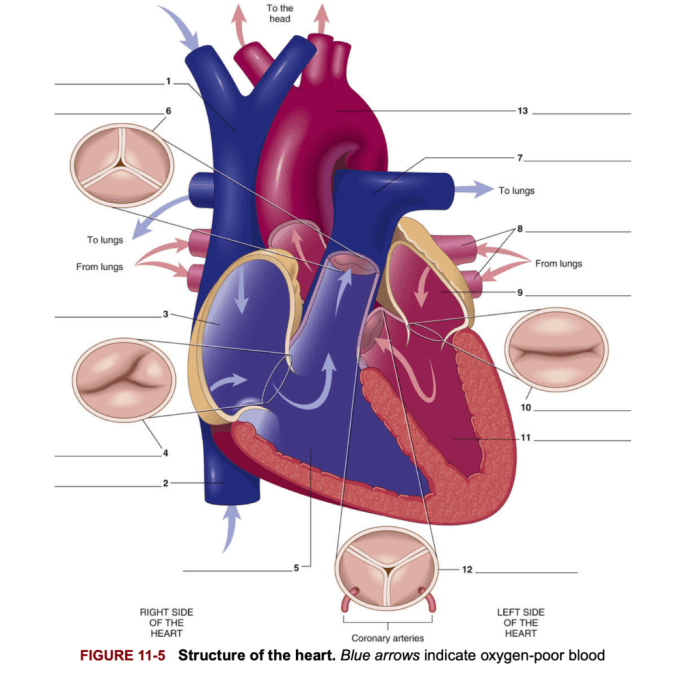
1.2 Blood Vessels
Blood vessels are tubes that carry blood throughout the body. Arteries carry blood away from the heart, while veins carry blood back to the heart. Capillaries are the smallest blood vessels and allow for the exchange of oxygen and nutrients between the blood and tissues.
1.3 Blood
Blood is a fluid tissue that contains red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. Red blood cells carry oxygen, white blood cells fight infection, platelets help with blood clotting, and plasma transports nutrients and hormones.
2. Cardiac Cycle and Regulation of Heart Rate
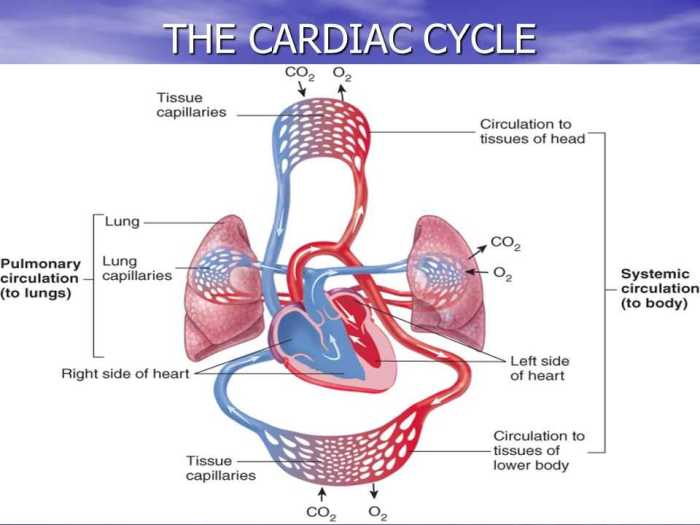
The cardiac cycle is the sequence of events that occur during one heartbeat. It consists of two main phases: systole (contraction) and diastole (relaxation).
2.1 The Cardiac Cycle, Chapter 11 the cardiovascular system answer key
- Atrial systole:The atria contract, pushing blood into the ventricles.
- Ventricular systole:The ventricles contract, pumping blood out to the body.
- Atrial diastole:The atria relax, allowing blood to flow into them.
- Ventricular diastole:The ventricles relax, allowing blood to flow into them.
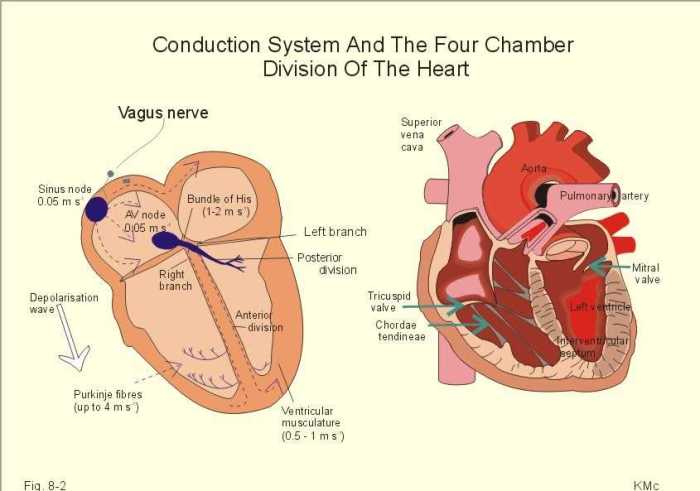
2.2 Regulation of Heart Rate
The heart rate is regulated by a combination of neural and hormonal mechanisms.
- Neural regulation:The autonomic nervous system (ANS) consists of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions. The sympathetic division increases heart rate, while the parasympathetic division decreases heart rate.
- Hormonal regulation:Hormones such as adrenaline and noradrenaline can increase heart rate, while acetylcholine can decrease heart rate.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the main function of the cardiovascular system?
To pump blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells and removing waste products.
What are the three layers of the heart wall?
Epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium.
What is hypertension?
A condition characterized by abnormally high blood pressure.