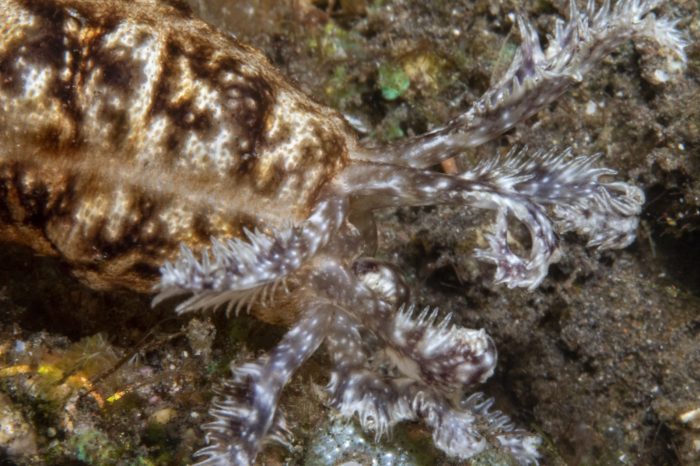
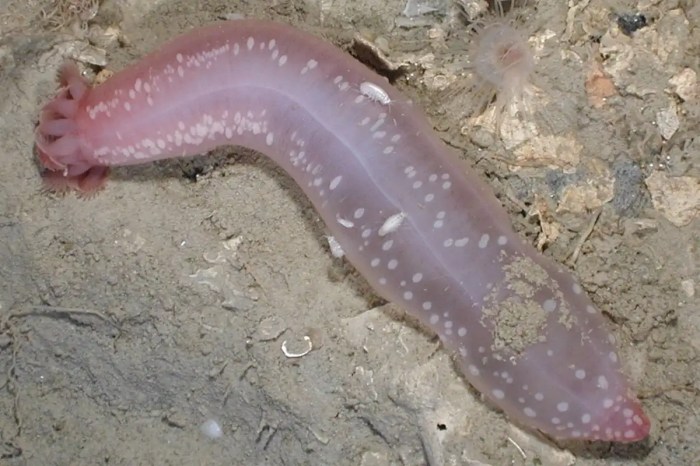
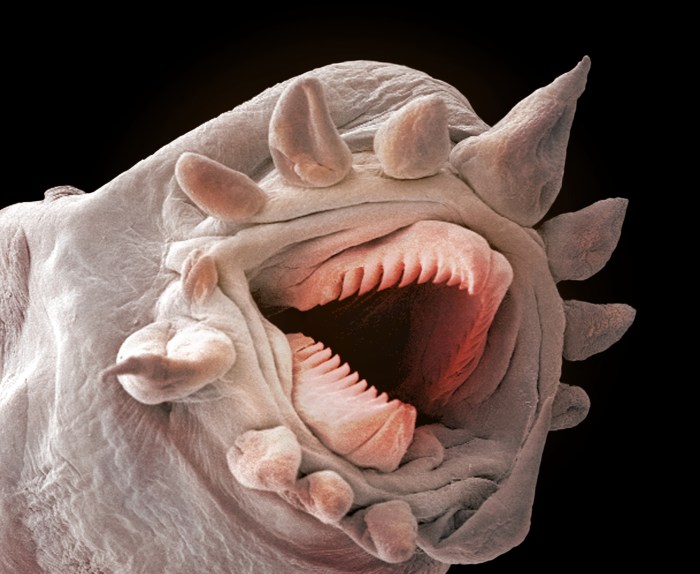
Club scale worm live on sea cucumbers – Club scale worms, remarkable creatures that inhabit the surfaces of sea cucumbers, exemplify the intricacies of symbiotic relationships in the marine realm. Their flattened bodies and adhesive structures allow them to cling tenaciously to their hosts, forming a mutually beneficial alliance that has fascinated scientists for decades.
Club scale worms are found in various marine habitats, ranging from shallow coastal waters to the depths of the ocean. Their geographical distribution spans across different regions of the globe, indicating their adaptability to diverse environmental conditions.
Introduction

Club scale worms are a unique group of polychaetes that live exclusively on sea cucumbers. They have a symbiotic relationship with their hosts, providing them with protection and food in exchange for transportation and access to nutrients. Club scale worms have a number of morphological adaptations that enable them to live on sea cucumbers, including flattened bodies and adhesive structures.
Habitat and Distribution
Club scale worms are found in a variety of marine habitats, including coral reefs, seagrass beds, and sandy bottoms. They are most commonly found in tropical and subtropical waters, but they can also be found in temperate regions. Club scale worms are distributed throughout the world, but they are most abundant in the Indo-Pacific region.
Physical Adaptations
Club scale worms have a number of morphological adaptations that enable them to live on sea cucumbers. Their bodies are flattened, which allows them to fit snugly against the body of their host. They also have a number of adhesive structures, including suckers and hooks, which help them to attach to the sea cucumber’s skin.
Feeding Behavior
Club scale worms are suspension feeders. They feed on plankton and other small particles that are suspended in the water column. They use their feathery gills to filter food particles from the water. Club scale worms can also feed on mucus and other secretions from their host sea cucumber.
Reproductive Strategies
Club scale worms have a complex life cycle that is synchronized with the life cycle of their host sea cucumber. They release their eggs and sperm into the water column, where they fertilize and develop into larvae. The larvae then settle on a sea cucumber and metamorphose into adults.
Ecological Interactions
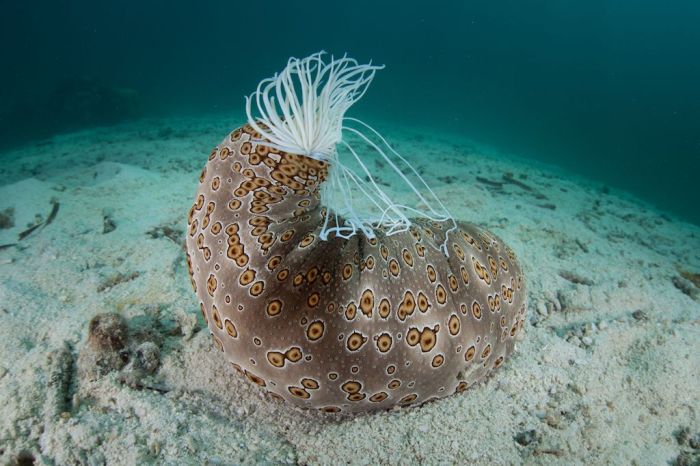
Club scale worms have a mutualistic relationship with sea cucumbers. The worms provide the sea cucumber with protection from predators and parasites, and the sea cucumber provides the worms with transportation and access to nutrients. Club scale worms can also help to clean the sea cucumber’s skin and remove parasites.
Conservation and Threats, Club scale worm live on sea cucumbers
Club scale worms are not currently considered to be threatened, but they are vulnerable to the same threats that face sea cucumbers. These threats include habitat loss, overfishing, and pollution. Club scale worms can also be affected by diseases that affect sea cucumbers.
Top FAQs: Club Scale Worm Live On Sea Cucumbers
What are the primary food sources for club scale worms?
Club scale worms primarily feed on mucus, detritus, and microorganisms present on the surface of their sea cucumber hosts.
How do club scale worms benefit from their symbiotic relationship with sea cucumbers?
The symbiotic relationship provides club scale worms with protection from predators, access to a stable food source, and a suitable environment for reproduction.
What are the conservation concerns surrounding club scale worms and sea cucumbers?
Overfishing of sea cucumbers, habitat destruction, and climate change pose potential threats to the populations of both club scale worms and their sea cucumber hosts.