Is CF2Cl2 ionic or molecular? Embark on a captivating journey to explore the fascinating world of chemical bonding and uncover the secrets behind this intriguing compound. Delve into the depths of ionic and molecular compounds, unraveling their distinct characteristics and properties.
Join us as we delve into the intricate details of CF2Cl2, deciphering its molecular structure and uncovering its diverse applications.
Prepare to be enlightened as we navigate the realm of chemistry, unraveling the mysteries surrounding CF2Cl2 and its unique properties.
Definition of Ionic and Molecular Compounds
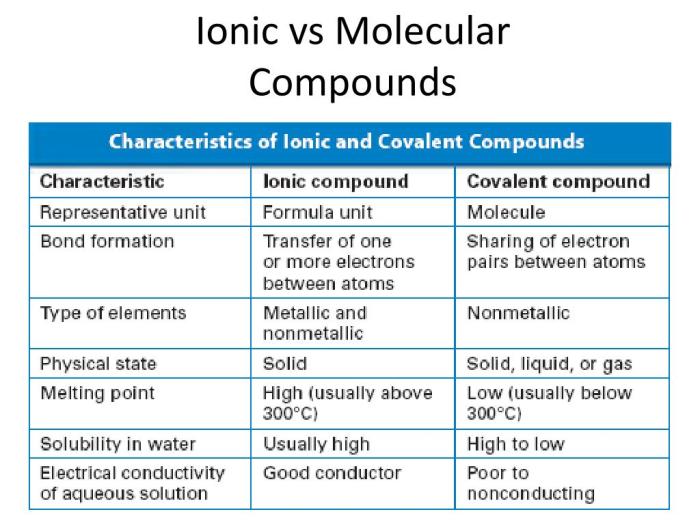
Ionic compounds are formed by the transfer of electrons from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of positively charged ions (cations) and negatively charged ions (anions). These ions are held together by electrostatic forces, forming a crystal lattice.
Examples of ionic compounds include sodium chloride (NaCl), potassium iodide (KI), and calcium oxide (CaO).Molecular compounds, on the other hand, are formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms. The shared electrons form covalent bonds, which hold the atoms together.
Is CF2Cl2 ionic or molecular? Well, it’s a molecular compound, meaning it’s made up of molecules that are held together by covalent bonds. If you’re looking for more information on this topic, check out the m tallman 2013 answer key . It provides a comprehensive overview of the topic, including its chemical structure and properties.
Molecular compounds typically exist as discrete molecules, rather than as a crystal lattice. Examples of molecular compounds include water (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), and methane (CH4).
Properties of CF2Cl2: Is Cf2cl2 Ionic Or Molecular
CF2Cl2, also known as dichlorodifluoromethane, is a colorless, non-flammable gas with a slightly sweet odor. It is a nonpolar molecule with a tetrahedral shape.
Physical Properties
- Molecular weight: 120.91 g/mol
- Melting point: -157.7 °C
- Boiling point: -29.8 °C
- Density: 1.49 g/L at 25 °C
Chemical Properties
- CF2Cl2 is a stable compound that is resistant to hydrolysis and oxidation.
- It reacts with strong bases to form salts of CF2Cl2-.
- It can undergo free radical reactions to form a variety of products.
Nonpolarity, Is cf2cl2 ionic or molecular
CF2Cl2 is a nonpolar molecule because the electronegativities of carbon, fluorine, and chlorine are similar. This means that the electrons in the C-F and C-Cl bonds are shared equally, resulting in a net zero dipole moment.
Bonding in CF2Cl2

CF2Cl2 is a nonpolar covalent compound. The carbon atom in CF2Cl2 is sp3 hybridized, and it forms three sigma bonds with the two fluorine atoms and one chlorine atom. The remaining sp3 hybrid orbital on the carbon atom overlaps with a p orbital on the other chlorine atom to form a pi bond.
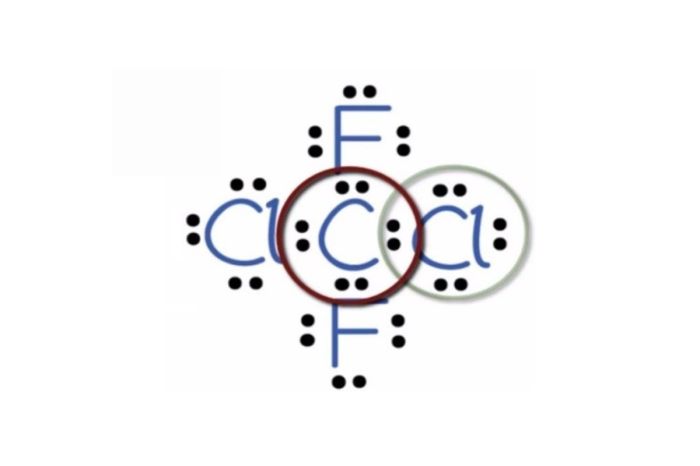
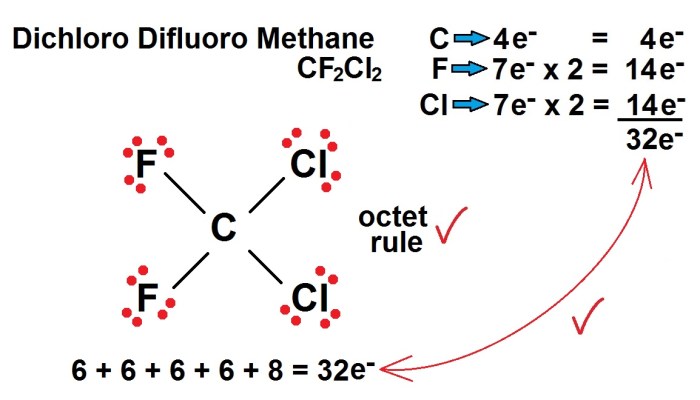
Lewis Structure
The Lewis structure of CF2Cl2 is:
:F:
:F-C-Cl:
:Cl:
Comparison to Other Compounds
CF2Cl2 shares similarities with other compounds like CH2Cl2 (dichloromethane) and CF4 (tetrafluoromethane), but there are also distinct differences in their bonding and properties.
CH2Cl2 vs. CF2Cl2
CH2Cl2 and CF2Cl2 both have a tetrahedral molecular geometry, but the electronegativity difference between carbon and chlorine in CH2Cl2 (2.5) is less than that between carbon and fluorine in CF2Cl2 (4.0). This results in more ionic character in CF2Cl2, leading to a higher dipole moment and stronger intermolecular forces.
CF4 vs. CF2Cl2
CF4 has a tetrahedral molecular geometry and nonpolar covalent bonds due to the high electronegativity of fluorine. In contrast, CF2Cl2 has a polar covalent bond between carbon and chlorine, resulting in a dipole moment and intermolecular forces. These differences contribute to the lower boiling point and higher reactivity of CF2Cl2 compared to CF4.
Applications of CF2Cl2
CF2Cl2, also known as R-12 or Freon-12, is widely used in various industrial applications due to its unique properties. It is commonly employed as a refrigerant, propellant, and blowing agent.
As a refrigerant, CF2Cl2 was extensively used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems before being phased out due to its ozone-depleting potential. Its effectiveness as a refrigerant stems from its ability to absorb and release heat efficiently, making it suitable for cooling applications.
Propellant
CF2Cl2 also finds application as a propellant in aerosol products, such as spray paints, hairsprays, and insecticides. Its inert nature and ability to create pressure make it an ideal propellant for these applications. However, due to environmental concerns, CF2Cl2 is being replaced by more environmentally friendly alternatives.
FAQs
Is CF2Cl2 an ionic compound?
No, CF2Cl2 is a molecular compound due to the covalent bonds between carbon and fluorine atoms.
Why is CF2Cl2 nonpolar?
The electronegativity difference between carbon and fluorine is relatively small, resulting in a symmetrical distribution of electrons and a nonpolar molecule.
