Dive into our meticulously crafted AP Biology Unit 3 Test PDF, your ultimate guide to mastering this crucial section of the exam. With a wealth of practice questions, expert tips, and engaging case studies, this resource will empower you to conquer Unit 3 with confidence.
Our comprehensive PDF covers all the key concepts and theories, organized in an easy-to-follow format. You’ll gain insights into the structure and format of the exam, ensuring you’re well-prepared for the challenges ahead.
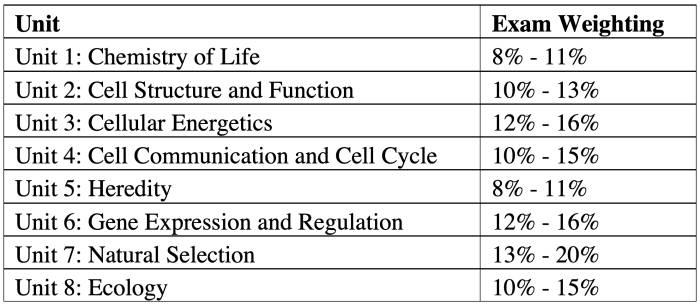
Topic Overview

AP Biology Unit 3 delves into the captivating realm of cellular processes, energy transfer, and heredity. This unit serves as a cornerstone in understanding the fundamental mechanisms that govern the functioning of life.Unit 3 is structured to provide a comprehensive examination of essential biological concepts.
It encompasses topics such as cellular respiration, photosynthesis, cell communication, cell cycle, and meiosis. The unit test is designed to assess students’ grasp of these concepts through a combination of multiple-choice questions, short answer responses, and data analysis tasks.
Study Resources

In Unit 3, having a comprehensive understanding of the complex topics is crucial. To aid in your preparation, utilizing reputable sources and engaging with practice materials can significantly enhance your learning experience.
Identifying Reputable Sources
Reliable sources are essential for obtaining accurate and up-to-date information. When selecting study materials, consider the following:
-
-*Author’s Credentials
Check the author’s expertise and affiliation with reputable institutions.
-*Publication Date
Ensure the material is recent and aligns with the latest scientific advancements.
-*Peer Review
Look for sources that have undergone peer review, indicating their validity and credibility.
Benefits of Practice Tests and Sample Questions
Practice tests and sample questions offer numerous advantages:
-
-*Identify Knowledge Gaps
They pinpoint areas where you need further reinforcement.
-*Familiarize with Exam Format
Practice tests simulate the actual exam, helping you adapt to the time constraints and question styles.
-*Improve Time Management
By practicing under timed conditions, you enhance your ability to allocate time effectively.
-*Boost Confidence
Successfully completing practice questions can build your confidence and reduce test anxiety.
Study Resource Comparison Table
To guide your study resource selection, consider the following table comparing different options:| Resource | Pros | Cons ||—|—|—||
*Official Course Textbook | Comprehensive and aligned with the curriculum | Can be expensive and bulky |
|
When you’re done with the AP Biology Unit 3 test PDF, why not take a break and check out some nbme 11 answers step 2 ? It’s a great way to test your knowledge and see where you stand. And who knows, you might even learn something new! Then, come back and finish strong with the rest of the AP Biology Unit 3 test PDF.
*Online Platforms (e.g., Khan Academy, Crash Course) | Free and accessible; engaging videos and interactive simulations | May lack depth and rigor |
|
*Practice Test Books | Provide realistic practice questions | Limited to specific test formats |
|
*Tutoring Services | Personalized guidance and support | Can be costly and may not be readily available |
Exam Preparation Strategies: Ap Biology Unit 3 Test Pdf

Succeeding in the AP Biology Unit 3 exam requires not only a solid understanding of the concepts but also effective test-taking strategies. This section will provide you with essential tips to help you manage your time, reduce anxiety, and approach different question types with confidence.
Time Management, Ap biology unit 3 test pdf
Time management is crucial during the exam. To optimize your time:
- Preview the entire exam and allocate time for each section based on its weight.
- Read the instructions carefully for each question and skip questions you’re unsure about initially.
- Return to skipped questions later if time permits.
- Avoid spending too much time on any one question.
Anxiety Management
Anxiety can interfere with your performance. To manage anxiety:
- Prepare thoroughly to build confidence.
- Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation.
- Get a good night’s sleep before the exam.
- Arrive at the exam early to familiarize yourself with the testing environment.
Question Types
The AP Biology Unit 3 exam includes various question types. Here’s how to approach each type:
Multiple Choice
- Read the question and answer choices carefully.
- Eliminate obviously incorrect answers.
- Consider the context of the question and use your knowledge to select the best answer.
Free Response
- Read the question thoroughly and identify the key concepts.
- Organize your response logically, using headings and paragraphs.
- Support your claims with evidence from the course material.
Data Analysis
- Examine the data provided and identify any trends or patterns.
- Use statistical tools, such as means and standard deviations, to analyze the data.
- Draw conclusions based on your analysis and support them with evidence.
Content Analysis
Unit 3 of AP Biology delves into the intricacies of heredity and evolution, providing a comprehensive understanding of the fundamental principles that govern the inheritance and variation of traits in living organisms. The unit explores key concepts such as Mendelian genetics, molecular genetics, and evolutionary mechanisms, laying the foundation for comprehending the diversity and unity of life.
The following table summarizes the main topics covered in Unit 3 and highlights their significance in understanding the field of biology:
| Topic | Importance |
|---|---|
| Mendelian Genetics | Establishes the fundamental principles of inheritance, including the concepts of dominant and recessive alleles, segregation, and independent assortment. |
| Molecular Genetics | Explores the structure and function of DNA and RNA, providing insights into the molecular basis of heredity and the mechanisms of gene expression. |
| Evolution | Examines the mechanisms and patterns of evolutionary change over time, including natural selection, genetic drift, and speciation. |
| Interconnections Between Topics | Recognizing the interconnectedness of these topics is crucial for a holistic understanding of biology. Mendelian genetics provides the foundation for understanding the inheritance of traits, while molecular genetics delves into the molecular mechanisms underlying these patterns. Evolutionary mechanisms, in turn, explain how these inherited traits change over time, shaping the diversity and adaptation of species. |
Sample Test Questions
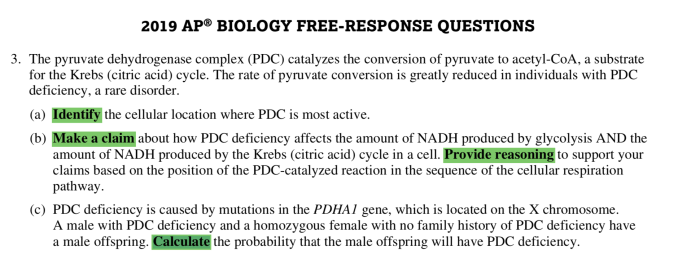
This section provides a comprehensive set of sample test questions to assist in your preparation for Unit 3 of AP Biology. These questions cover the core concepts and key ideas from the unit and are organized by topic to facilitate targeted practice.
Each question is accompanied by a detailed answer explanation to reinforce your understanding of the material and provide insights into the types of questions you may encounter on the actual exam.
Cell Communication
- Local and long-distance signaling pathways:Signal transduction pathways can be classified based on the distance over which the signal is transmitted. Local signaling involves direct contact between cells or neighboring cells, while long-distance signaling involves the transmission of signals over longer distances through chemical messengers.
- Receptor proteins:Receptor proteins are molecules located on the surface of cells that bind to specific signaling molecules and initiate intracellular responses. They can be classified into various types based on their structure and mechanism of action.
- Signal transduction pathways:Signal transduction pathways are a series of molecular events that occur within cells in response to the binding of a signaling molecule to a receptor protein. These pathways often involve multiple steps, including signal amplification and the activation of specific target molecules.
- Second messengers:Second messengers are small molecules or ions that are generated within cells in response to the activation of receptor proteins. They act as intracellular messengers and relay the signal to downstream targets, such as enzymes or transcription factors.
- G proteins:G proteins are a family of proteins that play a crucial role in signal transduction pathways. They act as molecular switches that bind to guanine nucleotides (GDP or GTP) and undergo conformational changes that regulate their activity.
Cell Cycle
- Phases of the cell cycle:The cell cycle is divided into four distinct phases: G1, S, G2, and M. Each phase is characterized by specific cellular processes and checkpoints that ensure the proper progression of the cell cycle.
- Cell cycle checkpoints:Cell cycle checkpoints are regulatory mechanisms that monitor the progress of the cell cycle and ensure that critical events occur in the correct order. These checkpoints can halt the cell cycle if conditions are not favorable for cell division.
- Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases:Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are key regulators of the cell cycle. Cyclins bind to CDKs and activate them, which in turn phosphorylate specific target proteins and drive the cell cycle forward.
- Cancer and the cell cycle:Dysregulation of the cell cycle can lead to uncontrolled cell division and cancer. Mutations in genes encoding cell cycle regulators can disrupt the normal progression of the cell cycle and contribute to cancer development.
Meiosis
- Stages of meiosis:Meiosis is a specialized form of cell division that occurs in reproductive cells and results in the production of gametes (eggs and sperm). It involves two rounds of division, meiosis I and meiosis II, each consisting of specific stages.
- Genetic recombination:Genetic recombination is a process that occurs during meiosis and involves the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. This process generates genetic diversity and contributes to the variation observed in offspring.
- Independent assortment:Independent assortment is the random distribution of homologous chromosomes during meiosis. This ensures that each gamete receives a unique combination of chromosomes, further increasing genetic diversity.
- Consequences of nondisjunction:Nondisjunction is an error in chromosome segregation that can occur during meiosis. It can lead to the production of gametes with an abnormal number of chromosomes, which can result in developmental abnormalities or genetic disorders.
Mendelian Genetics
- Mendelian principles of inheritance:Mendelian genetics is the study of the inheritance of traits based on the principles proposed by Gregor Mendel. These principles include the law of segregation, the law of independent assortment, and the law of dominance.
- Punnett squares:Punnett squares are a tool used to predict the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring based on the genotypes of the parents. They are constructed by arranging the alleles of the parents along the sides of the square and filling in the boxes with the possible combinations of alleles.
- Pedigree analysis:Pedigree analysis is a method used to trace the inheritance of traits within a family. Pedigree charts are constructed using symbols to represent individuals and their relationships, and they can be used to identify patterns of inheritance and predict the likelihood of an individual inheriting a particular trait.
- Extensions of Mendelian genetics:Mendelian genetics has been extended to include concepts such as incomplete dominance, codominance, and multiple alleles. These extensions explain the inheritance patterns of traits that do not follow simple dominant-recessive relationships.
Molecular Genetics
- Structure of DNA:DNA is a double-stranded molecule composed of nucleotides linked by phosphodiester bonds. Each nucleotide consists of a nitrogenous base, a deoxyribose sugar, and a phosphate group.
- Replication of DNA:DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA. It occurs during the S phase of the cell cycle and involves the unwinding of the DNA double helix and the synthesis of new strands complementary to the original strands.
- Transcription:Transcription is the process by which RNA is synthesized from a DNA template. It occurs in the nucleus and involves the unwinding of the DNA double helix and the synthesis of an RNA molecule complementary to one of the DNA strands.
- Translation:Translation is the process by which proteins are synthesized from an RNA template. It occurs in the cytoplasm and involves the ribosome reading the RNA molecule and assembling amino acids in the correct order to form a protein.
Case Studies
Case studies provide an immersive approach to understanding the intricate interplay of Unit 3 concepts. They allow students to apply their knowledge to real-world scenarios, fostering critical thinking and analytical skills.
To design an effective case study, incorporate multiple Unit 3 concepts such as molecular biology, genetics, and evolution. The case should present a complex problem or phenomenon that can be examined through the lens of these concepts.
Guiding Case Study Analysis
When analyzing a case study, students should focus on identifying the relevant concepts, applying them to the problem, and drawing connections between the different aspects of the case.
- Identify Concepts:Determine which Unit 3 concepts are applicable to the case study and how they relate to the problem.
- Apply Concepts:Use the identified concepts to analyze the case, explain the underlying mechanisms, and support arguments.
- Draw Connections:Explore how the different concepts interact and contribute to the overall understanding of the case.
Exam Relevance
Case studies can serve as excellent preparation for the exam by providing a practical context for applying Unit 3 concepts. By analyzing case studies, students can develop a deeper understanding of how these concepts are interconnected and applied in real-world situations.
Implications for Understanding Unit 3 Material
Case studies offer a valuable opportunity to reinforce and expand students’ understanding of Unit 3 material. They challenge students to think critically, integrate knowledge from different concepts, and apply their understanding to novel situations.
FAQ Summary
What topics are covered in Unit 3 of AP Biology?
Unit 3 encompasses topics such as cellular respiration, photosynthesis, genetics, and molecular biology.
How can I effectively prepare for the Unit 3 exam?
Utilize our comprehensive PDF, which provides practice questions, study tips, and exam strategies tailored to Unit 3.
What types of questions can I expect on the exam?
The exam includes multiple-choice, free-response, and case-based questions covering the key concepts of Unit 3.